Visualize BIOM data with boxplots.
Usage
taxa_boxplot(
biom,
x = NULL,
rank = -1,
layers = "x",
taxa = 6,
unc = "singly",
other = FALSE,
p.top = Inf,
stat.by = x,
facet.by = NULL,
colors = TRUE,
shapes = TRUE,
patterns = FALSE,
flip = FALSE,
stripe = NULL,
ci = "ci",
level = 0.95,
p.adj = "fdr",
outliers = NULL,
xlab.angle = "auto",
p.label = 0.05,
transform = "none",
y.transform = "sqrt",
caption = TRUE,
...
)Arguments
- biom
An rbiom object, or any value accepted by
as_rbiom().- x
A categorical metadata column name to use for the x-axis. Or
NULL, which puts taxa along the x-axis. Default:NULL- rank
What rank(s) of taxa to display. E.g.
"Phylum","Genus",".otu", etc. An integer vector can also be given, where1is the highest rank,2is the second highest,-1is the lowest rank,-2is the second lowest, and0is the OTU "rank". Runbiom$ranksto see all options for a given rbiom object. Default:-1.- layers
One or more of
c("bar", "box" ("x"), "violin", "dot", "strip", "crossbar", "errorbar", "linerange", "pointrange"). Single letter abbreviations are also accepted. For instance,c("box", "dot")is equivalent toc("x", "d")and"xd". Default:"x"- taxa
Which taxa to display. An integer value will show the top n most abundant taxa. A value 0 <= n < 1 will show any taxa with that mean abundance or greater (e.g.
0.1implies >= 10%). A character vector of taxa names will show only those named taxa. Default:6.- unc
How to handle unclassified, uncultured, and similarly ambiguous taxa names. Options are:
"singly"-Replaces them with the OTU name.
"grouped"-Replaces them with a higher rank's name.
"drop"-Excludes them from the result.
"asis"-To not check/modify any taxa names.
Abbreviations are allowed. Default:
"singly"- other
Sum all non-itemized taxa into an "Other" taxa. When
FALSE, only returns taxa matched by thetaxaargument. SpecifyingTRUEadds "Other" to the returned set. A string can also be given to implyTRUE, but with that value as the name to use instead of "Other". Default:FALSE- p.top
Only display taxa with the most significant differences in abundance. If
p.topis >= 1, then thep.topmost significant taxa are displayed. Ifp.topis less than one, all taxa with an adjusted p-value <=p.topare displayed. Recommended to be used in combination with thetaxaparameter to set a lower bound on the mean abundance of considered taxa. Default:Inf- stat.by
Dataset field with the statistical groups. Must be categorical. Default:
NULL- facet.by
Dataset field(s) to use for faceting. Must be categorical. Default:
NULL- colors
How to color the groups. Options are:
TRUE-Automatically select colorblind-friendly colors.
FALSEorNULL-Don't use colors.
- a palette name -
Auto-select colors from this set. E.g.
"okabe"- character vector -
Custom colors to use. E.g.
c("red", "#00FF00")- named character vector -
Explicit mapping. E.g.
c(Male = "blue", Female = "red")
See "Aesthetics" section below for additional information. Default:
TRUE- shapes
Shapes for each group. Options are similar to
colors's:TRUE,FALSE,NULL, shape names (typically integers 0 - 17), or a named vector mapping groups to specific shape names. See "Aesthetics" section below for additional information. Default:TRUE- patterns
Patterns for each group. Options are similar to
colors's:TRUE,FALSE,NULL, pattern names ("brick","chevron","fish","grid", etc), or a named vector mapping groups to specific pattern names. See "Aesthetics" section below for additional information. Default:FALSE- flip
Transpose the axes, so that taxa are present as rows instead of columns. Default:
FALSE- stripe
Shade every other x position. Default: same as flip
- ci
How to calculate min/max of the crossbar, errorbar, linerange, and pointrange layers. Options are:
"ci"(confidence interval),"range","sd"(standard deviation),"se"(standard error), and"mad"(median absolute deviation). The center mark of crossbar and pointrange represents the mean, except for"mad"in which case it represents the median. Default:"ci"- level
The confidence level for calculating a confidence interval. Default:
0.95- p.adj
Method to use for multiple comparisons adjustment of p-values. Run
p.adjust.methodsfor a list of available options. Default:"fdr"- outliers
Show boxplot outliers?
TRUEto always show.FALSEto always hide.NULLto only hide them when overlaying a dot or strip chart. Default:NULL- xlab.angle
Angle of the labels at the bottom of the plot. Options are
"auto",'0','30', and'90'. Default:"auto".- p.label
Minimum adjusted p-value to display on the plot with a bracket.
p.label = 0.05-Show p-values that are <= 0.05.
p.label = 0-Don't show any p-values on the plot.
p.label = 1-Show all p-values on the plot.
If a numeric vector with more than one value is provided, they will be used as breaks for asterisk notation. Default:
0.05- transform
Transformation to apply to calculated values. Options are:
c("none", "rank", "log", "log1p", "sqrt", "percent")."rank"is useful for correcting for non-normally distributions before applying regression statistics. Default:"none"- y.transform
The transformation to apply to the y-axis. Visualizing differences of both high- and low-abundance taxa is best done with a non-linear axis. Options are:
"sqrt"-square-root transformation
"log1p"-log(y + 1) transformation
"none"-no transformation
These methods allow visualization of both high- and low-abundance taxa simultaneously, without complaint about 'zero' count observations. Default:
"sqrt"Usexaxis.transformoryaxis.transformto pass custom values directly to ggplot2'sscale_*functions.- caption
Add methodology caption beneath the plot. Default:
TRUE- ...
Additional parameters to pass along to ggplot2 functions. Prefix a parameter name with a layer name to pass it to only that layer. For instance,
d.size = 2ensures only the points on the dot layer have their size set to2.
Value
A ggplot2 plot. The computed data points, ggplot2 command,
stats table, and stats table commands are available as $data,
$code, $stats, and $stats$code, respectively.
Aesthetics
All built-in color palettes are colorblind-friendly. The available
categorical palette names are: "okabe", "carto", "r4",
"polychrome", "tol", "bright", "light",
"muted", "vibrant", "tableau", "classic",
"alphabet", "tableau20", "kelly", and "fishy".
Patterns are added using the fillpattern R package. Options are "brick",
"chevron", "fish", "grid", "herringbone", "hexagon", "octagon",
"rain", "saw", "shingle", "rshingle", "stripe", and "wave",
optionally abbreviated and/or suffixed with modifiers. For example,
"hex10_sm" for the hexagon pattern rotated 10 degrees and shrunk by 2x.
See fillpattern::fill_pattern() for complete documentation of options.
Shapes can be given as per base R - numbers 0 through 17 for various shapes, or the decimal value of an ascii character, e.g. a-z = 65:90; A-Z = 97:122 to use letters instead of shapes on the plot. Character strings may used as well.
See also
Other taxa_abundance:
sample_sums(),
taxa_clusters(),
taxa_corrplot(),
taxa_heatmap(),
taxa_stacked(),
taxa_stats(),
taxa_sums(),
taxa_table()
Other visualization:
adiv_boxplot(),
adiv_corrplot(),
bdiv_boxplot(),
bdiv_corrplot(),
bdiv_heatmap(),
bdiv_ord_plot(),
plot_heatmap(),
rare_corrplot(),
rare_multiplot(),
rare_stacked(),
stats_boxplot(),
stats_corrplot(),
taxa_corrplot(),
taxa_heatmap(),
taxa_stacked()
Examples
library(rbiom)
biom <- rarefy(hmp50)
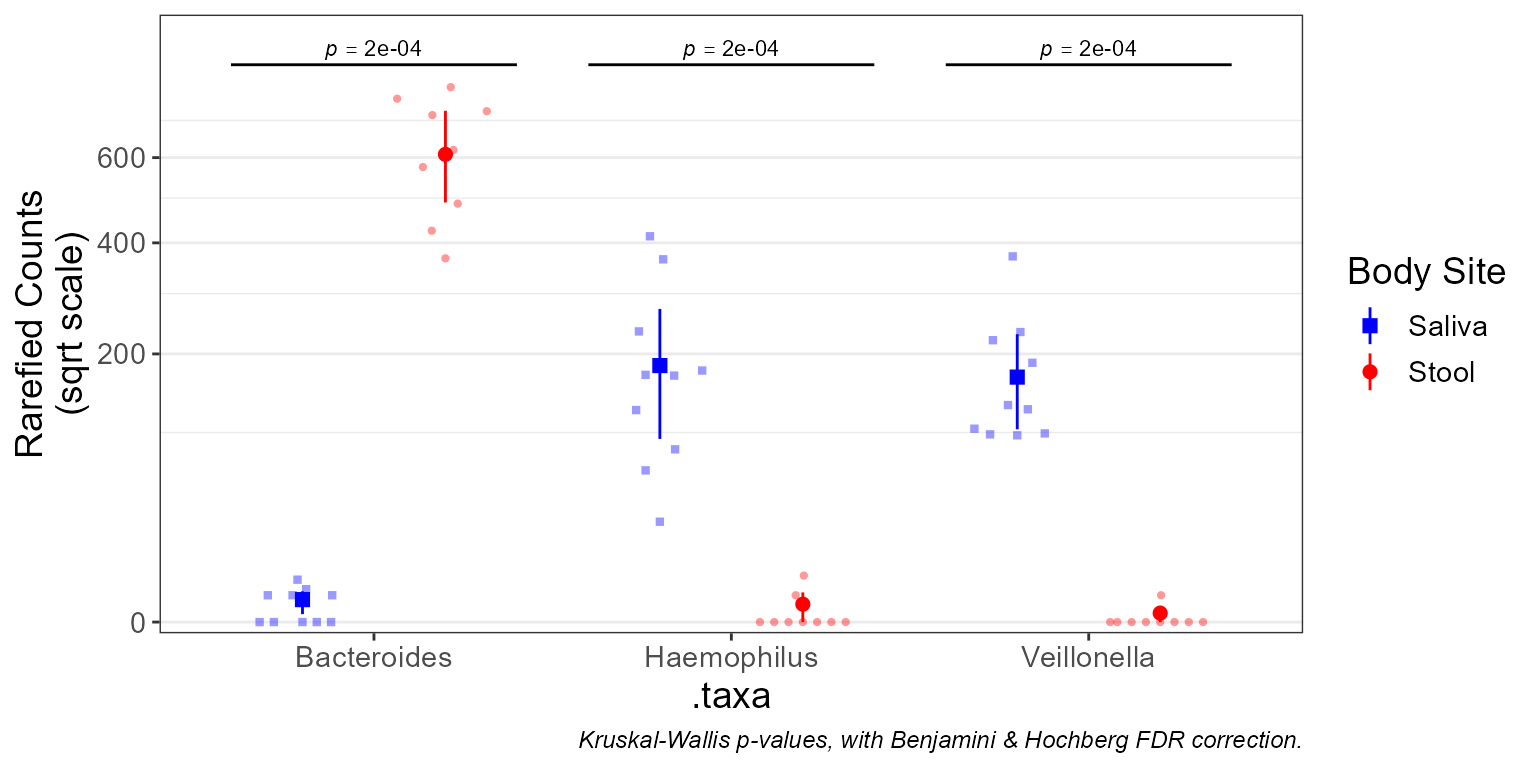
taxa_boxplot(biom, stat.by = "Body Site", stripe = TRUE)
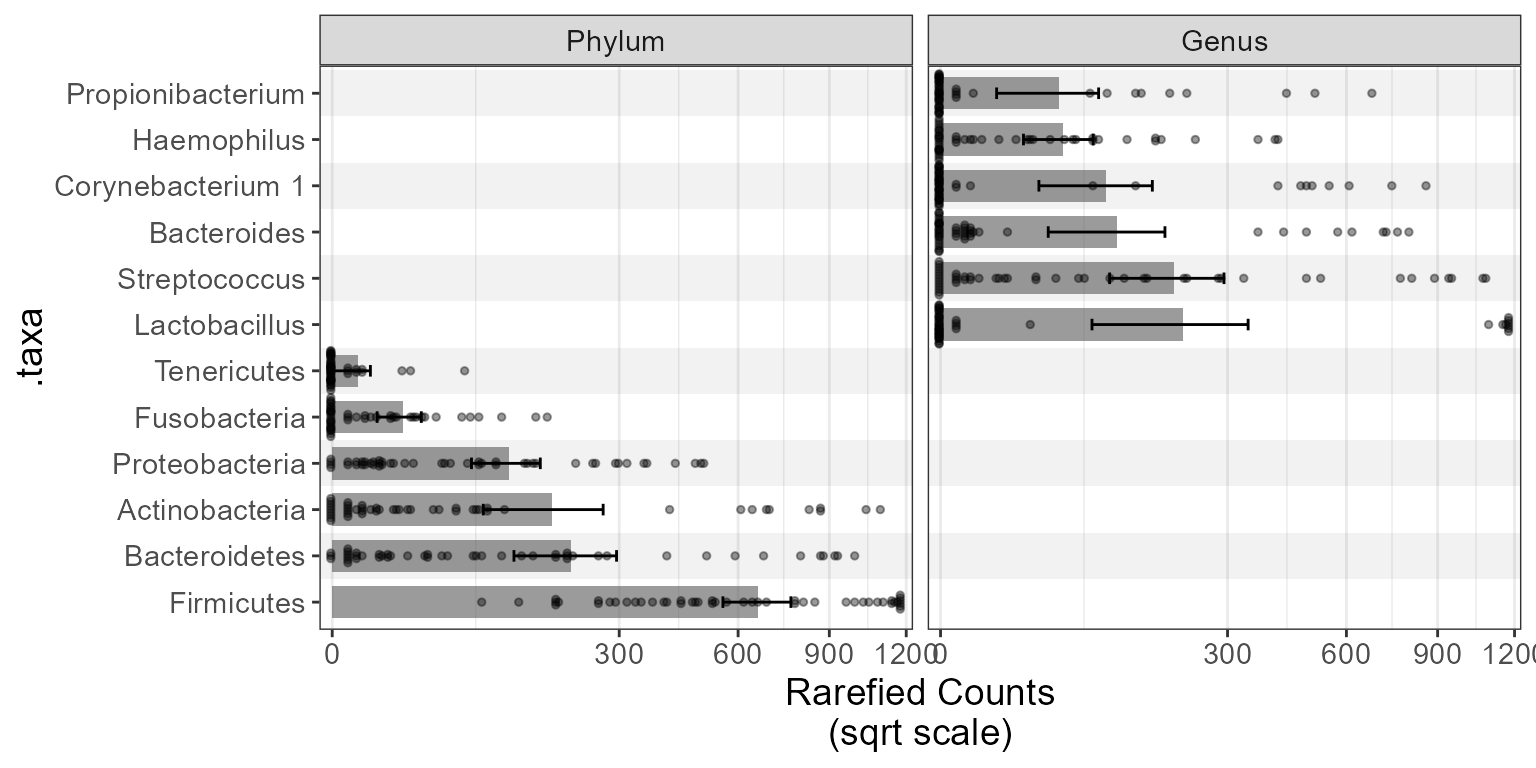
 taxa_boxplot(biom, layers = "bed", rank = c("Phylum", "Genus"), flip = TRUE)
taxa_boxplot(biom, layers = "bed", rank = c("Phylum", "Genus"), flip = TRUE)
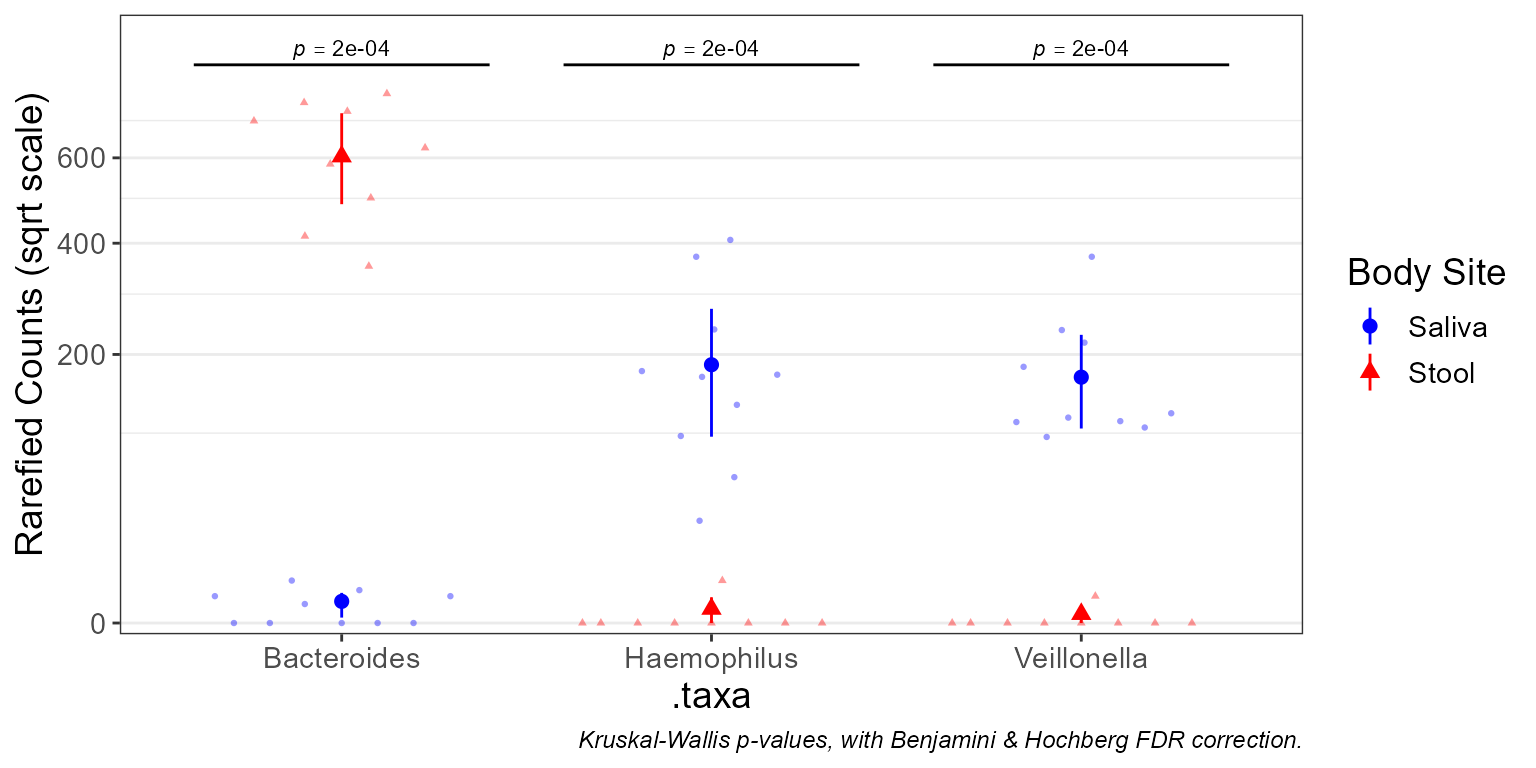
 taxa_boxplot(
biom = subset(biom, `Body Site` %in% c('Saliva', 'Stool')),
taxa = 3,
layers = "ps",
stat.by = "Body Site",
colors = c('Saliva' = "blue", 'Stool' = "red") )
taxa_boxplot(
biom = subset(biom, `Body Site` %in% c('Saliva', 'Stool')),
taxa = 3,
layers = "ps",
stat.by = "Body Site",
colors = c('Saliva' = "blue", 'Stool' = "red") )